Electromagnetic Simulation Software
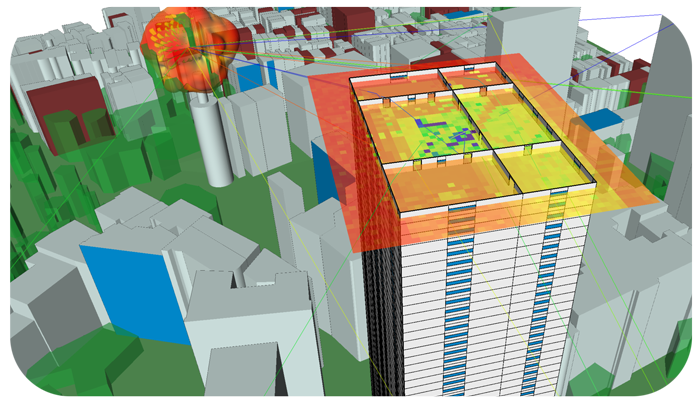
Providing Solutions for Design Engineers and EM Simulation Professionals for 30 Years.
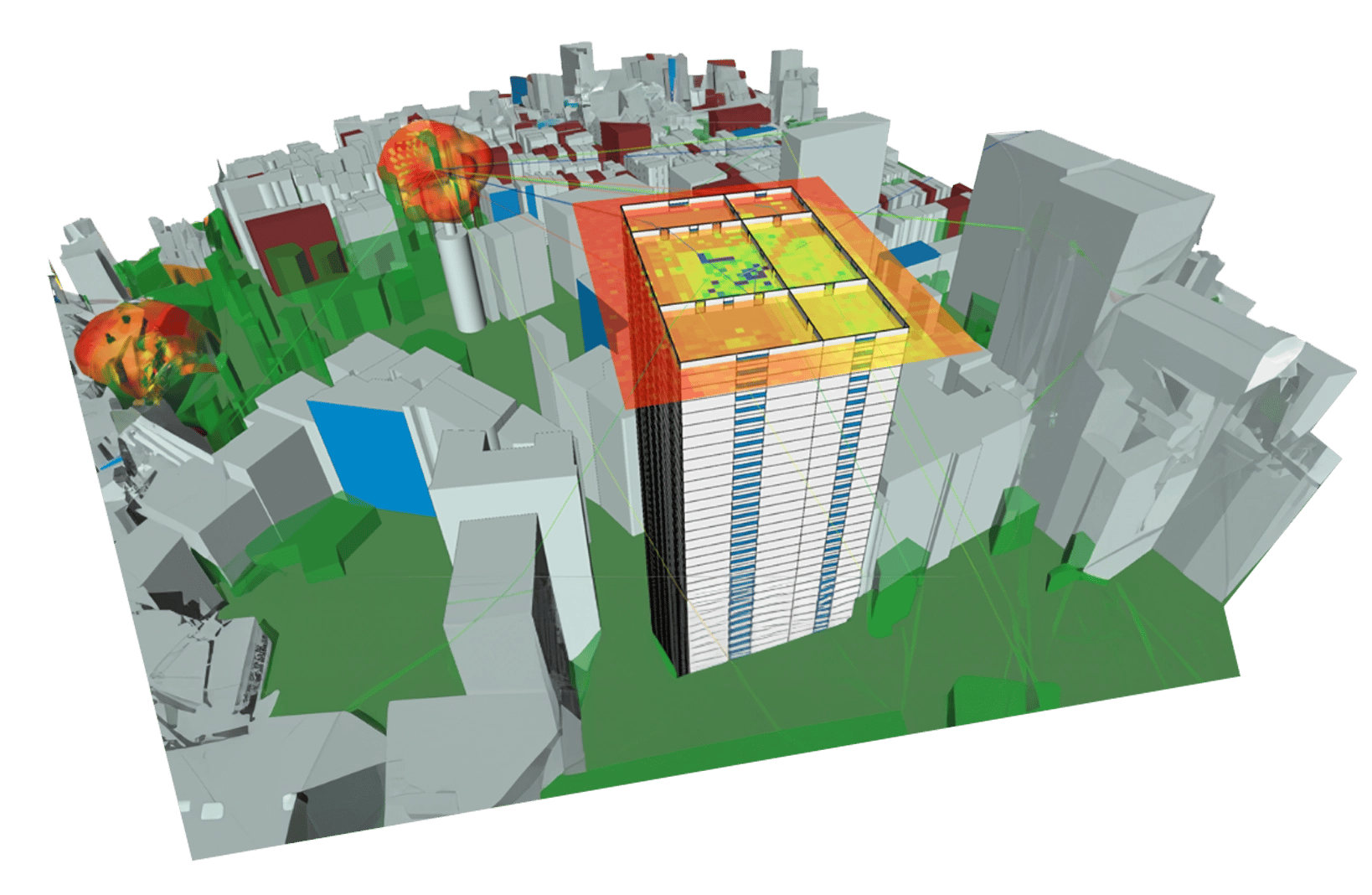
In Need of a Customized Solution to Your Most Complex EM Challenges?

Innovative electromagnetic simulation software and exceptional support to reduce the time and cost of delivering your devices to market.
Leading provider of electromagnetic simulation software for 30 years
Versatile tools and agile structure
Remcom provides innovative electromagnetic simulation software and wireless propagation software for commercial users and U.S. government sponsors. Remcom’s suite of complementary products work together to provide complete end-to-end design and analysis of complex devices in real world scenarios, simplifying EM analysis for a wide variety of applications including antenna design and placement,
- 5G MIMO
- Outdoor and indoor mmWave planning
- Mobile device design
- Biological effects
- Microwave device analysis
- Automotive radar
...and more
Remcom Software
Remcom’s products are designed to work together to provide complete and accurate results.
-
XFdtd®
3D Electromagnetic Simulation Software -
Wireless InSite®
3D Wireless Prediction Software -
WaveFarer®
Radar Simulation Software -
XGtd®
Far Zone Radiation, RCS, and EMI/EMC for Electrically-Large Platforms
-
XFdtd® 3D Electromagnetic Simulation Software
XFdtd 3D EM Simulation Software provides engineers with powerful tools to shorten development time and release products to market sooner. A full-featured electromagnetic simulation solver, XFdtd outpaces other methods in efficiency as the number of unknowns increases.
Learn More About XFdtd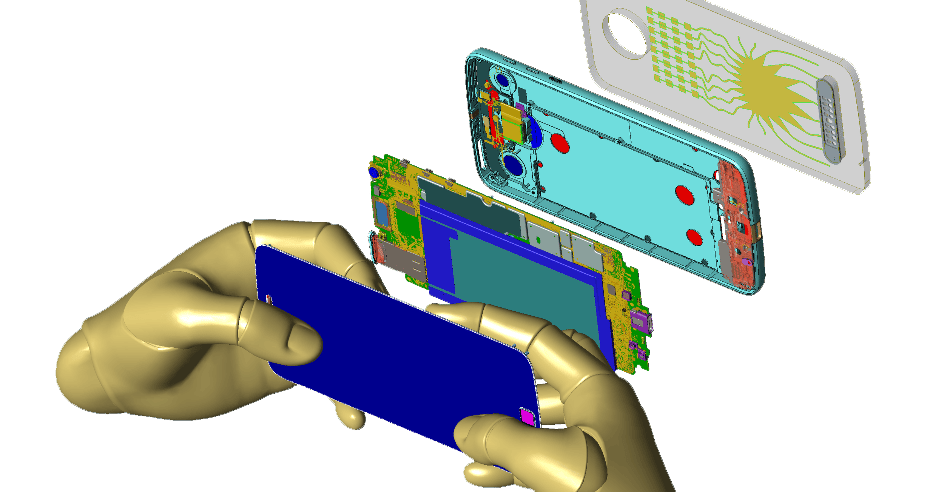
-
Wireless InSite® 3D Wireless Prediction Software
Wireless InSite is a suite of RF propagation models, providing 3D ray-tracing, fast ray-based methods, and empirical models for the analysis of site-specific radio wave propagation and wireless communication systems. Through its combined modeling, simulation, and post-processing capabilities, it provides efficient and accurate predictions of EM propagation and communication channel characteristics in complex urban, indoor, rural and mixed path environments.
Learn More About Wireless InSite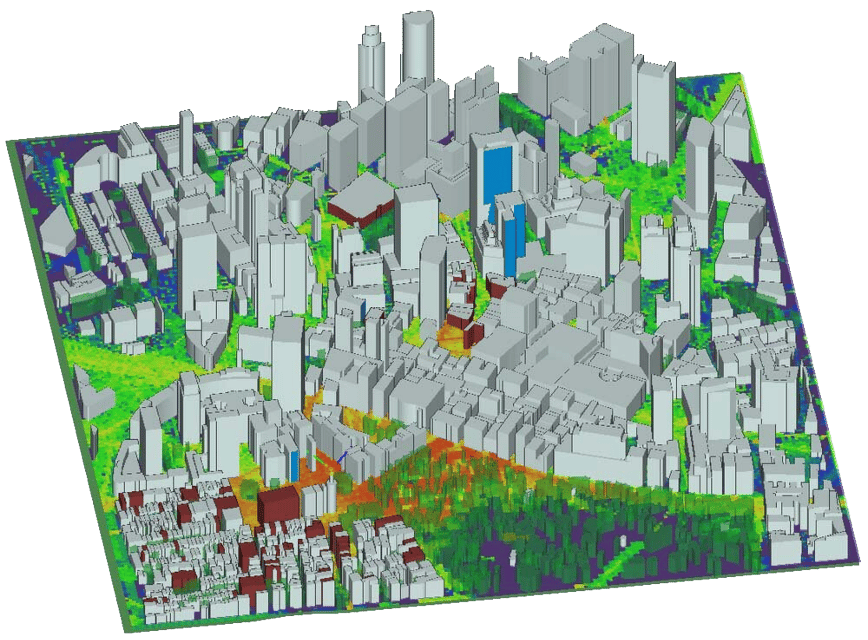
-
WaveFarer® Radar Simulation Software
WaveFarer is a high fidelity radar simulator that accounts for multipath and scattering from structures and vehicles in the immediate environment of a radar system as well as key atmospheric and scattering effects for frequencies up to and beyond 100 GHz. Applications include simulation of automotive drive scenarios, indoor sensors, and far field radar cross section (RCS).
Learn More About WaveFarer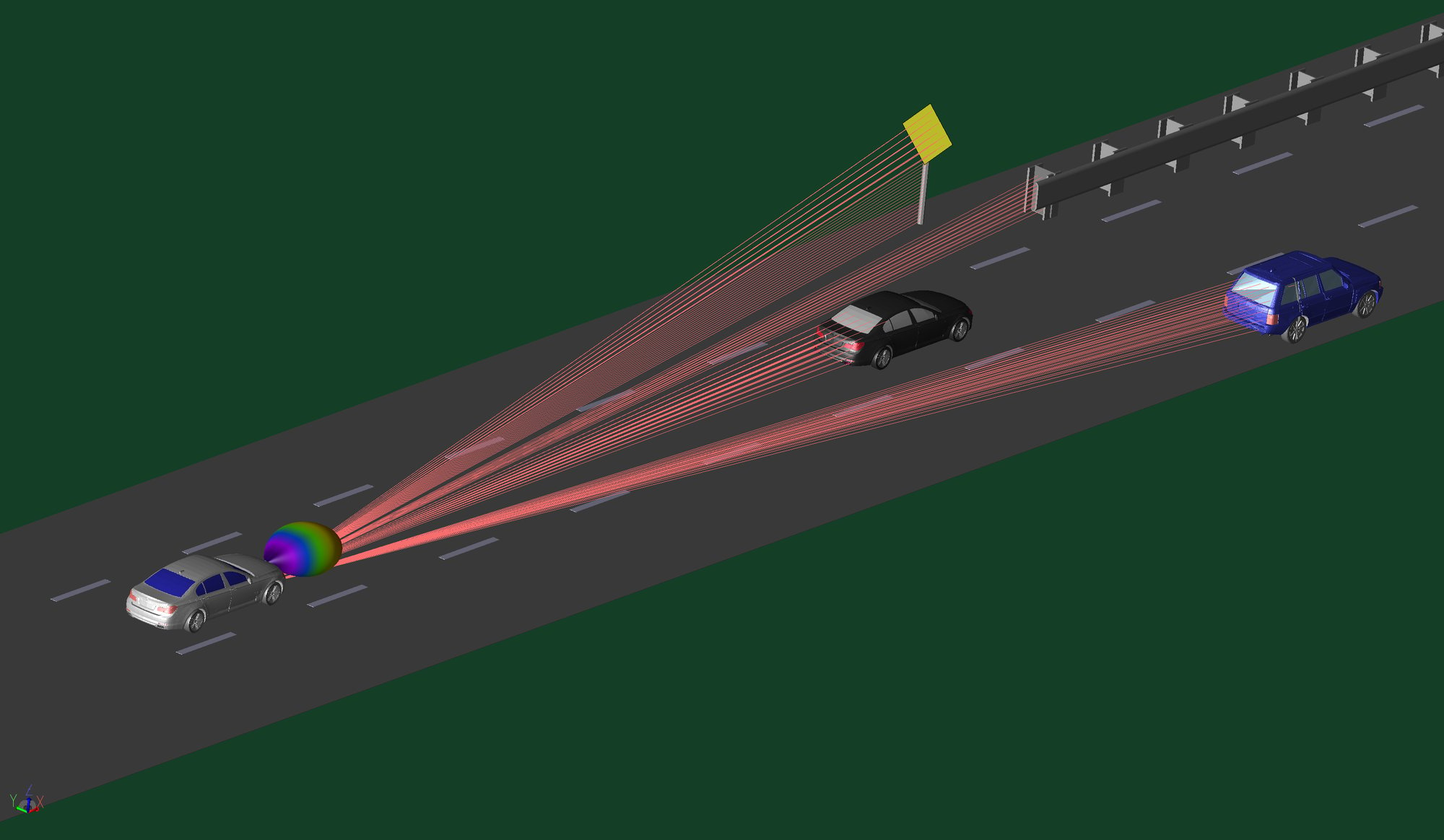
-
XGtd® Far Zone Radiation, RCS, and EMI/EMC for Electrically-Large Platforms
XGtd is a ray-based electromagnetic analysis tool for assessing the effects of a vehicle or vessel on antenna radiation, predicting coupling between antennas, and predicting radar cross section (RCS). It is ideally suited for applications with higher frequencies or very large platforms where the requirements of a full physics method may exceed available computational resources.
Learn More About XGtd
Applications
Simplify your work and improve your products.
Remcom’s EM analysis products are used for antenna design and analysis, bio/EM effects, MRI, microwave circuits, RFID, military and defense applications, EMI/EMC, and more.

5G MIMO
Remcom’s EM simulation software provides a complete 5G solution, from system and MIMO antenna design through performance assessment in realistic, simulated environments, and planning for deployment in 5G networks. Our mission is to provide accurate solutions so customers can reliably predict how their systems will behave in the real world.
5G MIMO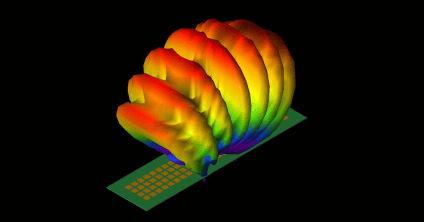
Antenna Design
Antenna technology is constantly advancing to meet the growing demands of industry. Likewise, Remcom has been keeping pace in order to provide engineers with antenna simulation software that matches their processes and helps them meet their device design requirements.
Antenna Design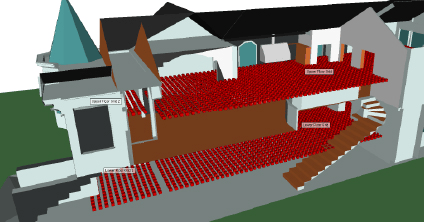
Antenna Placement
Remcom’s antenna modeling software tools ensure proper design and placement of antennas in almost any application. Our simulation tools can work alone or together for a complete analysis of how an antenna will perform.
Antenna Placement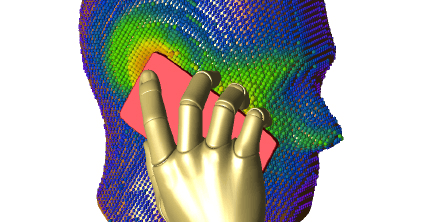
Mobile Device
Precision is key when designing today’s complex mobile devices, and engineers can’t afford discrepancies between device efficiency and simulation results. Remcom users see less than a 0.5 dB difference in device efficiency when compared to electromagnetic simulation results.
Mobile Device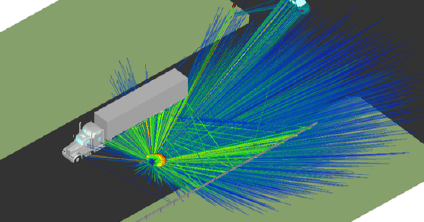
Automotive Radar
Simulation technology has advanced to meet more stringent design requirements for 24 GHz and 77 GHz automotive radar sensors including blind spot detection (BSD) and lane change assistance (LCA). Remcom offers an integrated approach from sensor design to drive test scenarios.
Automotive Radar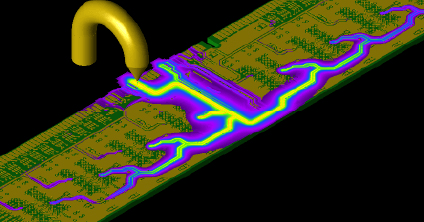
ESD Testing
Utilizing XFdtd's electrostatic discharge testing simulations allows engineers to pinpoint locations susceptible to ESD damage and optimize ESD mitigation during the concept and design stage of product development.
ESD Testing
An Enjoyable Business Collaboration — it’s just as important as the software you choose.
The Remcom Difference
Customer Focused
Remcom is devoted to listening to our customers and understanding their needs, building requested features directly into the software with each new release. And since we’ve been providing EM expertise and solutions since electromagnetic field simulation software became a reality, you can be confident that many years of experience have gone into the design and functionality of the products we create and the way we support them.
Some of the clients that trust us:
Featured Resources
Explore our resources to learn how our products can simplify your EM analysis projects.
Save time and reduce costs.
Contact Remcom today for a customized solution to your most complex electromagnetic challenges.
Request a Quote











